Openssl Generate Csr From Existing Private Key
OpenSSL CSR Wizard
Our OpenSSL CSR Wizard is the fastest way to create your CSR for Apache (or any platform) using OpenSSL.
Fill in the details, click Generate, then paste your customized OpenSSL CSR command in to your terminal.
Note: After 2015, certificates for internal names will no longer be trusted.
Common Name (Server Name) The fully qualified domain name that clients will use to reach your server. For example, to secure https://www.example.com, your common name must be www.example.com or *.example.com for a wildcard certificate. Although less common, you may also enter the public IP address of your server. Department (optional) You can leave this field blank. This is the department within your organization that you want to appear on the certificate. It will be listed in the certificate's subject as Organizational Unit, or 'OU'. Common examples: Web Administration, Web Security, or Marketing City The city where your organization is legally located. State or Province The state or province where your organization is legally located. Country We guessed your country based on your IP address, but if we guessed wrong, please choose the correct country. If your country does not appear in this list, there is a chance we cannot issue certificates to organizations in your country. Organization name The exact legal name of your organization, (e.g., DigiCert, Inc.) If you do not have a legal registered organization name, you should enter your own full name here. Key RSA Key sizes smaller than 2048 are considered unsecure. Now just copy and paste this command into a terminal session on your server. Your CSR will be written to ###FILE###.csr. |
- Sep 11, 2018 You apply by generating a CSR with a key pair on your server that would, ideally, hold the SSL certificate. The CSR contains crucial organization details which the CA verifies. Generate a CSR and key pair locally on your server. The key pair consists of a public and private key.
- $ openssl req -out codesigning.csr -key private.key -new. Where private.key is the existing private key. As you can see you do not generate this CSR from your certificate (public key). Also you do not generate the 'same' CSR, just a new one to request a new certificate.
- One of the most versatile SSL tools is OpenSSL which is an open source implementation of the SSL protocol. There are versions of OpenSSL for nearly every platform, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. OpenSSL is commonly used to create the CSR and private key.
After you've created a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and ordered your certificate, you still need to install the SSL certificate on your server.
For instructions on how to install SSL certificates, see SSL Certificate Installation Instructions & Tutorials.
Where do I paste this command?
Using Microsoft IIS to generate CSR and Private Key. A CSR in Microsoft IIS 7; 2. Back Up Private Key; 3. Convert to RSA Private Key Format; You can also use Microsoft IIS to generate a Private Key and CSR. How to generate a CSR in Microsoft IIS 7. Openssl-win32binopenssl.cfg openssl pkcs12 -in filename.pfx -nocerts -out key.pem.
You can run this command wherever you have OpenSSL available—most likely on your server, but you can also run it on your own computer since macOS comes with OpenSSL installed. Just make sure you keep track of your private key file after you create your CSR; you'll need that private key to install your certificate.
What happens when I run this command?
OpenSSL creates both your private key and your certificate signing request, and saves them to two files: your_common_name.key, and your_common_name.csr. You can then copy the contents of the CSR file and paste it into the CSR text box in our order form.
What kind of certificate should I buy?
If you want an SSL certificate for Apache, your best options are Standard certificates and Wildcard certificates.
A DigiCert Wildcard can protect all server names on your domain (e.g., *.example.com,). Our unlimited server license lets you protect all your servers for just one price. Many of our customers save thousands of dollars per year by using a DigiCert Wildcard certificate.
| Per Year Pricing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Years | $653 per year | ($1,307) | (You Save 10%) | |
| 1 Year | $688 | |||
Standard certificates are able to protect one server name (e.g., mail.example.com). If you only need SSL for one hostname, a Standard certificate will work perfectly.
| Per Year Pricing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Years | $207 per year | ($414) | (You Save 10%) | |
| 1 Year | $218 | |||
What If I Need Subject Alternative Names?
Multi-Domain (SAN) certificates allow you to assign multiple host names—known as Subject Alternative Names or SANs—in one certificate.
Using OpenSSL to Add Subject Alternative Names to a CSR is a complicated task. Our advice is to skip the hassle, use your most important server name as the Common Name in the CSR, and then specify the other names during the order process. Our Multi-Domain (SAN) certificate ordering process allows you to specify all the names you need without making you include them in the CSR.
You can also use OpenSSL to create a certificate request for your code signing certificate.
Si desea información en español a Hacer un CSR Utilizando OpenSSL.
Related:
- Learn more about what our Wildcard certificate can do for you.
- We also have a similar CSR Tool for Exchange 2007.
- Related Questions & Answers
- Selected Reading
OpenSSL is a CLI (Command Line Tool) which can be used to secure the server to generate public key infrastructure (PKI) and HTTPS. This article helps you as a quick reference to understand OpenSSL commands which are very useful in common, and for everyday scenarios especially for system administrators.
Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs)
If we want to obtain SSL certificate from a certificate authority (CA), we must generate a certificate signing request (CSR). A CSR consists of mainly the public key of a key pair, and some additional information. Both these components are merged into the certificate whenever we are signing for the CSR.
While generating a CSR, the system will prompt for information regarding the certificate and this information is called as Distinguished Name (DN). The important field in the DN is the Common Name (CN) which should be the FQND (Fully Qualified Domain Name) of the server or the host where we intend to use the certificate with.
The next item in a DN is to provide the additional information about our business or organization. If we purchase an SSL certificate from a certificate authority (CA), it is very important and required that these additional fields like “Organization” should reflect your organization for details.
Here is a general example for the CSR information prompt, when we run the OpenSSL command to generate the CSR.
We can also provide the information by non-interactive answers for the CSR information generation, we can do this by adding the –subj option to any OpenSSL commands that we try to generate or run.
Below is an example for the –subj option where we can provide the information of the organization where we want to use this CSR.
Generating CSRs
In this section, we will cover about OpenSSL commands which are related to generating the CSR. This CSR can be used to request an SSL certificate from a certificate authority.
Generate a Private Key and a CSR
If we want to use HTTPS (HTTP over TLS) to secure the Apache or Nginx web servers (using a Certificate Authority (CA) to issue the SSL certificate). Also, the ‘.CSR’ which we will be generating has to be sent to a CA for requesting the certificate for obtaining CA-signed SSL.
Below is the command to create a 2048-bit private key for ‘domain.key’ and a CSR ‘domain.csr’ from the scratch.
The ‘–newkey rsa:2048’ is the option which we are specifying that the key should be 2048-bit using the RSA algorithm. The ’ –nodes’ option is to specifying that the private key should not be encrypted with a pass phrase. The ‘-new’ option, indicates that a CSR is being generated.
Openssl Generate Csr From Private Key
Generate a CSR from an Existing Private Key
How To Generate Private Key
Here we will learn about, how to generate a CSR for which you have the private key.
Below is the command to create a new .csr file based on the private key which we already have.
Generate a CSR from an Existing Certificate and Private key
Here we can generate or renew an existing certificate where we miss the CSR file due to some reason. Here, the CSR will extract the information using the .CRT file which we have.
Below is the example for generating –
Where -x509toreq is specified that we are using the x509 certificate files to make a CSR.
Generating a Self-Singed Certificates
Here we will generate the Certificate to secure the web server where we use the self-signed certificate to use for development and testing purpose.
Here, we generate self-signed certificate using –x509 option, we can generate certificates with a validity of 365 days using –days 365 and a temporary .CSR files are generated using the above information.
Viewing the Certificates Files
Please note that, CSR files are encoded with .PEM format (which is not readable by the humans). This is required to view a certificate. In this section, we can cover the OpenSSL commands which are encoded with .PEM files.
Viewing CSR Files Entires
The below command will be used to view the contents of the .CRT files Ex (domain.crt) in the plain text format.
Working with Private Keys
Jenkins generate ssh key mac. In this section, will see how to use OpenSSL commands that are specific to creating and verifying the private keys.
Create a Private Key
Below is the command to create a password-protected and, 2048-bit encrypted private key file (ex. domain.key) –
Enter a password when prompted to complete the process.
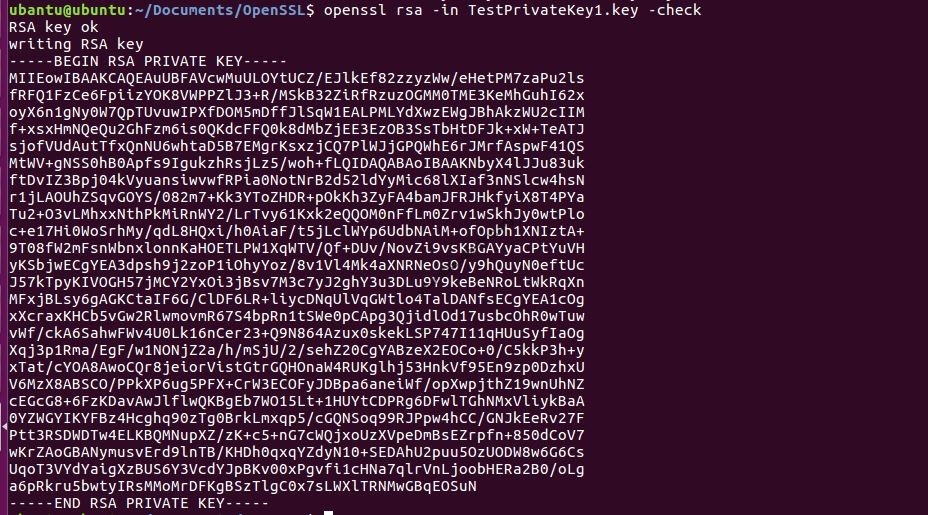
Verify a Private Key
Below is the command to check that a private key which we have generated (ex: domain.key) is a valid key or not
If the private key is encrypted, you will be prompted to enter the pass phrase. Upon the successful entry, the unencrypted key will be the output on the terminal.
In this article, we have learnt some commands and usage of OpenSSL commands which deals with SSL certificates where the OpenSSL has lots of features. We will learn more features and usage in the future. I hope this article will help us to understand some basic features of the OpenSSL.